Techno-Economic Optimization Of A Novel Stand-Alone Renewables-Based Electric Vehicle Charging Station In Qatar
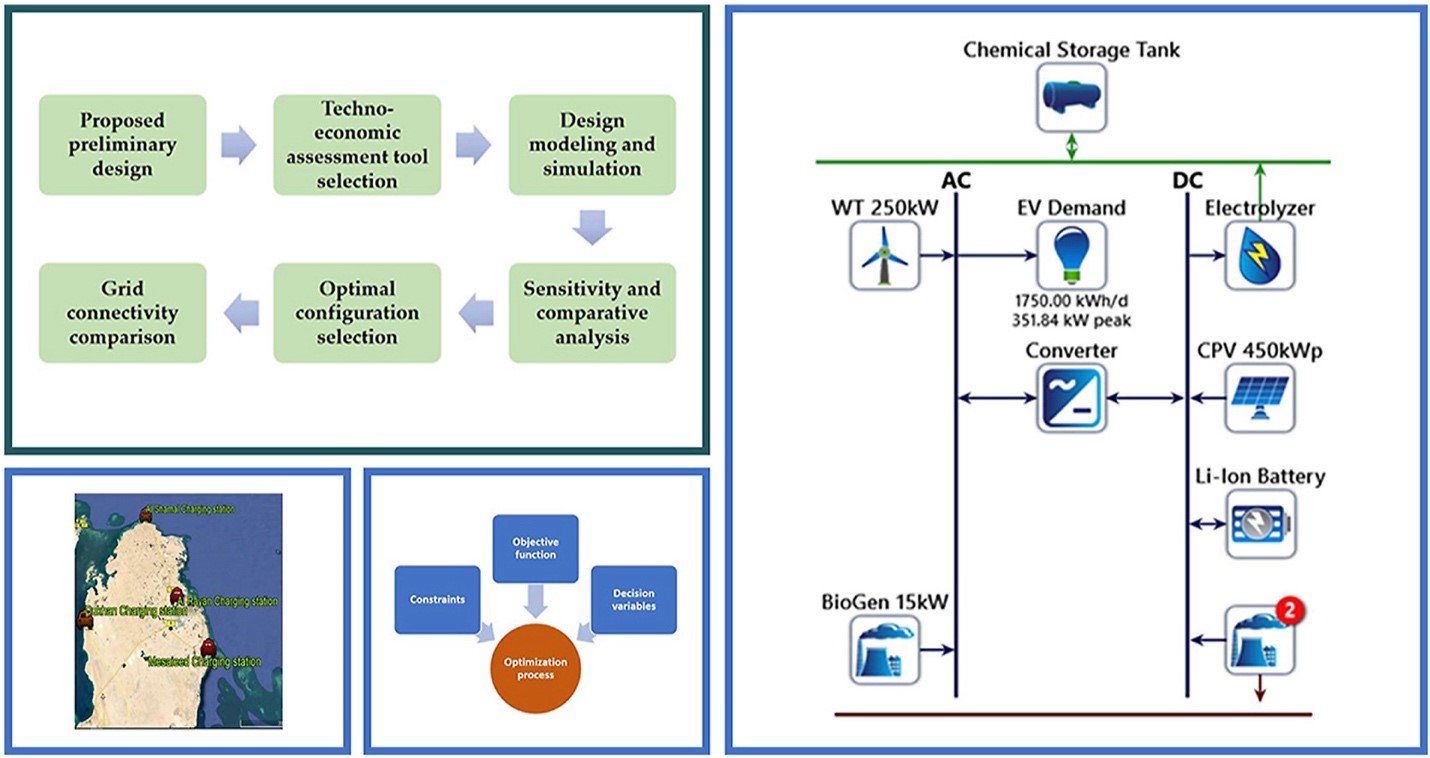
One of the main challenges of e-mobility roll-out is securing the required charging demand without stressing the existing power grid. The electrical source must be non-conventional to achieve the ultimate eco-friendly goal. This study conducts a techno-economic assessment for a novel stand-alone renewables-based charging station to determine the optimal configuration to generate the required daily charging demand. The optimization is accomplished through modeling and simulating of the proposed design using HOMER software in four cities of Qatar to investigate various geographical locations and metrological conditions. The optimal solution is compared with the grid extension option in each location using a comprehensive economic criterion. The results showed that 250 kW wind turbine with 60 m hub height, 450 kWp CPV/T system, 500 kW electrolyzer, 100 kW H2 and NH3 FCs, 15 kW bio-generator, 200 kg chemical storage tank, 304–324 kW Li-ion battery storage and 299–335 kW converter combination is the optimal stand-alone configuration for the selected sites. The optimum cases’ net present cost ranges between $2.53 M to $2.92 M, and the cost of electricity ranges between $0.285 to $0.329 per kWh. The proposed optimization methodology is suitable for applications in any location, considering the metrological conditions of the site under study.
Research Highlights
Life Cycle Assessment Of Clean Ammonia Synthesis From Thermo-Catalytic Solar Cracking Of Liquefied Natural Gas
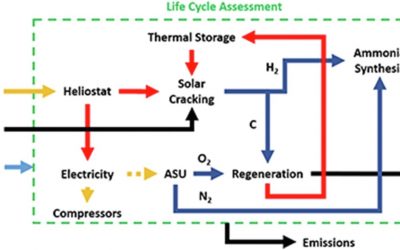
Ammonia is considered a sustainable energy storage medium with zero carbon content. In this work, thermal catalytic cracking of liquefied natural gas (LNG) at elevated temperatures employing concentrated solar tower is considered to produce clean hydrogen (CO2-free) and studied in terms of life cycle emissions.
Review On Cox-Free Hydrogen From Methane Cracking: Catalysts, Solar Energy Integration And Applications
Hydrogen fuel production from methane cracking is a sustainable process compared to the ones currently in practice due to minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon black that is co-produced is a valuable product and can be marketed to other industries.
SunReis (Sustainable Utilization of Novel Renewable Energy Integration & Storage)
SunReis (Sustainable Utilization of Novel Renewable Energy Integration & Storage) is a research group at Hamad Bin Khalifa University, Qatar, led by Dr. Yusuf Bicer. The acronym is derived from 'sunrays', where “reis” means leader/president in Arabic and Turkish. The group’s research interests include sustainability, energy storage, energy carriers, hydrogen, ammonia, integrated energy systems, cooling, desalination, carbon capture & management and renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and ocean.